深入了解 MySQL 的 JSON 数据类型(关系型数据库里的 NoSQL 初探)

SQL 数据库正趋向于严格。
如果使用过它们,你会同意数据库设计在实践中有很多坑这个说法,尽管它们看起来很容易。SQL 数据库的精髓是结构,因此被称为结构化查询语言。
另外一种视角看,我们拥有了 NoSQL 数据库,它灵活性好也被称为无模式数据库。在无模式数据库中,没有强迫的结构化限制,仅仅只要存储数据。
目录
尽管每个工具均有其使用范围,但有时需要混合搭配。
如果你可以构建数据库某部分并使其余部分充满灵活性,那会怎么样呢?
MySQL 5.7.8 版本
引入了一种 JSON 数据类型允许你实现以上功能。
本教程,你将学到。
- 如何使用 JSON 字段设计你的数据库表
- MYSQL 提供各种基于 JSON 的函数执行创建,阅读,更新和删除行操作。
- 如何在 Laravel 的 Eloquent ORM 中使用 JSON 字段
#为什么使用 JSON
此时,你可能会问自己,当 MySQL 引入 JSON 数据类型前已经满足了多样的数据库需求时,为什么还需要使用 JSON 。
答案在于你可能使用权宜的方法的一些场景。
让我通过一个案例来说明一下。
假设你正在构建一个 Web 应用程序,你必须在数据库中保存用户的配置或首选项。
通常,你可能会创建一个单独的数据库表,包含 id , user_id , key ,以及 value 字段,或者保存为一个格式化的字符串,在程序执行时再进行解析。
然而,这对于少量用户是很好的。如果你有 1000 个用户和 5 个配置项,则需要查看一个具有 5000 条记录的表,但这只是你应用非常小的一个功能。
或者你正在使用格式化的字符串,多余的解析代码只会增加服务器的负载。
这种情况下,使用 JSON 数据类型来保存用户的配置可以节省数据库表空间,并将单独保存的记录数减少到与用户数相同。
而且,你还能够获得不用编写任何 JSON 的解析代码的好处,因为 ORM 或者语言运行库会进行相应的处理。
# Schema
在我们深入使用 MySQL 中各种帅气的 JSON 特性之前,我们首先需要一个示例的数据库来继续下去。
所以,我们首先来解决数据库 Schema。
我们考虑将一个容纳多种品牌和各种电子设备的在线商店作为使用案例。
因为不同的电子设备有不同买家感兴趣的某些特性(比较 Macbook 和 Vacuumn Cleaner),所以通常使用 实体属性值模型 (EAV) 模式。
然而,我们现在可以选择使用 JSON 数据类型,因此我们放弃 EAV。
首先,我们的数据库被命名为e_store 并且只有三张表,分别是brands,categories,和 products。
我们的 brands 和 categories 表非常相似,都只有一个id和一个name字段。
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `e_store`
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8
DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
SET default_storage_engine = INNODB;
CREATE TABLE `e_store`.`brands`(
`id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL auto_increment ,
`name` VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
);
CREATE TABLE `e_store`.`categories`(
`id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL auto_increment ,
`name` VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
);这两张表的目的是容纳提供这些产品的产品分类和品牌信息。
当我们做完这些,接下来让我们往表里新增一些数据以便后续的使用。
/* Brands */
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`brands`(`name`)
VALUES
('Samsung');
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`brands`(`name`)
VALUES
('Nokia');
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`brands`(`name`)
VALUES
('Canon');
/* Types of electronic device */
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`categories`(`name`)
VALUES
('Television');
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`categories`(`name`)
VALUES
('Mobilephone');
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`categories`(`name`)
VALUES
('Camera');

接下来,是业务相关的教程。
我们将创建一个 products 表,这个表包含id, name, brand_id, category_id 和 attributes 字段。
CREATE TABLE `e_store`.`products`(
`id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT ,
`name` VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL ,
`brand_id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL ,
`category_id` INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL ,
`attributes` JSON NOT NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`) ,
INDEX `CATEGORY_ID`(`category_id` ASC) ,
INDEX `BRAND_ID`(`brand_id` ASC) ,
CONSTRAINT `brand_id` FOREIGN KEY(`brand_id`) REFERENCES `e_store`.`brands`(`id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE ,
CONSTRAINT `category_id` FOREIGN KEY(`category_id`) REFERENCES `e_store`.`categories`(`id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE CASCADE
);我们在表定义中为brand_id 和 category_id字段指定了外键约束,它们分别引用了brands 和 categories表。我们也指定了引用的行不允许删除,并且如果更新时,这些改变也会反映在引用里。
attributes字段的列类型已经被声明为 JSON,这是现在 MySQL 中一种可用的本地化数据类型。它允许我们在 MySQL 里给attributes字段使用各种与 JSON 相关的数据结构。
这是一份我们所创建数据库的实体关系图。
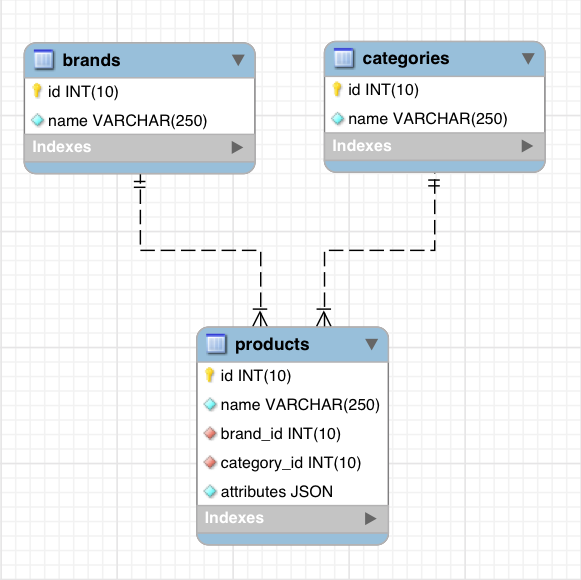
我们的数据库设计在效率和准确性上来说并不是最好的。
products表里没有价格列,并且我们将产品分成多个分类。然而,这个教程的目的并不是教授数据库设计,而是怎样在一个单独的表中使用 MySQL 的 JSON 特性对不同性质的对象建模。
# CRUD 操作
让我们来看看怎样在一个 JSON 字段中对数据进行创建、读取、更新和删除。
创建
在数据库中创建一条 JSON 记录非常简单。
你只需要在你的 Insert 语句中添加一条有效的 JSON 作为字段值。
/* Let's sell some televisions */
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Prime' ,
'1' ,
'1' ,
'{"screen": "50 inch", "resolution": "2048 x 1152 pixels", "ports": {"hdmi": 1, "usb": 3}, "speakers": {"left": "10 watt", "right": "10 watt"}}'
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Octoview' ,
'1' ,
'1' ,
'{"screen": "40 inch", "resolution": "1920 x 1080 pixels", "ports": {"hdmi": 1, "usb": 2}, "speakers": {"left": "10 watt", "right": "10 watt"}}'
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Dreamer' ,
'1' ,
'1' ,
'{"screen": "30 inch", "resolution": "1600 x 900 pixles", "ports": {"hdmi": 1, "usb": 1}, "speakers": {"left": "10 watt", "right": "10 watt"}}'
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Bravia' ,
'1' ,
'1' ,
'{"screen": "25 inch", "resolution": "1366 x 768 pixels", "ports": {"hdmi": 1, "usb": 0}, "speakers": {"left": "5 watt", "right": "5 watt"}}'
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Proton' ,
'1' ,
'1' ,
'{"screen": "20 inch", "resolution": "1280 x 720 pixels", "ports": {"hdmi": 0, "usb": 0}, "speakers": {"left": "5 watt", "right": "5 watt"}}'
);
你也可以使用内置的 JSON_OBJECT 函数来创建 JSON 对象。
JSON_OBJECT 函数接受 JSON_OBJECT(key1, value1, key2, value2, ... key(n), value(n)) 形式的键值对列表来返回一个 JSON 对象。
/* Let's sell some mobilephones */
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Desire' ,
'2' ,
'2' ,
JSON_OBJECT(
"network" ,
JSON_ARRAY("GSM" , "CDMA" , "HSPA" , "EVDO") ,
"body" ,
"5.11 x 2.59 x 0.46 inches" ,
"weight" ,
"143 grams" ,
"sim" ,
"Micro-SIM" ,
"display" ,
"4.5 inches" ,
"resolution" ,
"720 x 1280 pixels" ,
"os" ,
"Android Jellybean v4.3"
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Passion' ,
'2' ,
'2' ,
JSON_OBJECT(
"network" ,
JSON_ARRAY("GSM" , "CDMA" , "HSPA") ,
"body" ,
"6.11 x 3.59 x 0.46 inches" ,
"weight" ,
"145 grams" ,
"sim" ,
"Micro-SIM" ,
"display" ,
"4.5 inches" ,
"resolution" ,
"720 x 1280 pixels" ,
"os" ,
"Android Jellybean v4.3"
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Emotion' ,
'2' ,
'2' ,
JSON_OBJECT(
"network" ,
JSON_ARRAY("GSM" , "CDMA" , "EVDO") ,
"body" ,
"5.50 x 2.50 x 0.50 inches" ,
"weight" ,
"125 grams" ,
"sim" ,
"Micro-SIM" ,
"display" ,
"5.00 inches" ,
"resolution" ,
"720 x 1280 pixels" ,
"os" ,
"Android KitKat v4.3"
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Sensation' ,
'2' ,
'2' ,
JSON_OBJECT(
"network" ,
JSON_ARRAY("GSM" , "HSPA" , "EVDO") ,
"body" ,
"4.00 x 2.00 x 0.75 inches" ,
"weight" ,
"150 grams" ,
"sim" ,
"Micro-SIM" ,
"display" ,
"3.5 inches" ,
"resolution" ,
"720 x 1280 pixels" ,
"os" ,
"Android Lollypop v4.3"
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Joy' ,
'2' ,
'2' ,
JSON_OBJECT(
"network" ,
JSON_ARRAY("CDMA" , "HSPA" , "EVDO") ,
"body" ,
"7.00 x 3.50 x 0.25 inches" ,
"weight" ,
"250 grams" ,
"sim" ,
"Micro-SIM" ,
"display" ,
"6.5 inches" ,
"resolution" ,
"1920 x 1080 pixels" ,
"os" ,
"Android Marshmallow v4.3"
)
);
需要注意的是 JSON_ARRAY 函数接受到一组值会返回一个 JSON 数组。
如果多次指定相同的键,只会保留第一个键值对。这是 MySQL 内部对 JSON 的规范。 此外,作为规范的一部分,当对象被排序时,键值对之间的留白会被移除。
我们用来创建 JSON 对象的另一个函数是JSON_MERGE。
JSON_MERGE函数接受多个 JSON 对象,并生成一个单独的聚合对象。
/* 我们出售一些相机 */
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Explorer' ,
'3' ,
'3' ,
JSON_MERGE(
'{"sensor_type": "CMOS"}' ,
'{"processor": "Digic DV III"}' ,
'{"scanning_system": "progressive"}' ,
'{"mount_type": "PL"}' ,
'{"monitor_type": "LCD"}'
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Runner' ,
'3' ,
'3' ,
JSON_MERGE(
JSON_OBJECT("sensor_type" , "CMOS") ,
JSON_OBJECT("processor" , "Digic DV II") ,
JSON_OBJECT("scanning_system" , "progressive") ,
JSON_OBJECT("mount_type" , "PL") ,
JSON_OBJECT("monitor_type" , "LED")
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Traveler' ,
'3' ,
'3' ,
JSON_MERGE(
JSON_OBJECT("sensor_type" , "CMOS") ,
'{"processor": "Digic DV II"}' ,
'{"scanning_system": "progressive"}' ,
'{"mount_type": "PL"}' ,
'{"monitor_type": "LCD"}'
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Walker' ,
'3' ,
'3' ,
JSON_MERGE(
'{"sensor_type": "CMOS"}' ,
'{"processor": "Digic DV I"}' ,
'{"scanning_system": "progressive"}' ,
'{"mount_type": "PL"}' ,
'{"monitor_type": "LED"}'
)
);
INSERT INTO `e_store`.`products`(
`name` ,
`brand_id` ,
`category_id` ,
`attributes`
)
VALUES(
'Jumper' ,
'3' ,
'3' ,
JSON_MERGE(
'{"sensor_type": "CMOS"}' ,
'{"processor": "Digic DV I"}' ,
'{"scanning_system": "progressive"}' ,
'{"mount_type": "PL"}' ,
'{"monitor_type": "LCD"}'
)
);
在这些插入语句中发生了很多事情,这也许让人有些迷惑。然而,它很简单。
我们传递了一些对象给JSON_MERGE函数。这些对象中有些是由我们先前见过的JSON_OBJECT函数构造的,另一些被传递了 JSON 字符串。
在 JSON_MERGE 函数的情形下,如果一个键被重复添加多次,它的值会作为一个数组保留在输出中。
我想这是一个概念的验证。
/* output: {"network": ["GSM", "CDMA", "HSPA", "EVDO"]} */
SELECT JSON_MERGE(
'{"network": "GSM"}' ,
'{"network": "CDMA"}' ,
'{"network": "HSPA"}' ,
'{"network": "EVDO"}'
);我们可以使用提供字段值类型的 JSON_TYPE 函数来确认我们所有的查询已经成功执行。
/* output: OBJECT */
SELECT JSON_TYPE(attributes) FROM `e_store`.`products`;
读取
此时我们数据库里已经有一些产品数据供我们使用了。
对于非 JSON 类型的典型 MySQL 值,where 子句是非常直接的。只要指定列,运算符,和需要处理的值就行了。
尝试性的,当处理 JSON 列时,这样的 where 子句不起作用:
/* It's not that simple */
SELECT
*
FROM
`e_store`.`products`
WHERE
attributes = '{"ports": {"usb": 3, "hdmi": 1}, "screen": "50 inch", "speakers": {"left": "10 watt", "right": "10 watt"}, "resolution": "2048 x 1152 pixels"}';当你希望使用 JSON 字段来缩小行数时,你应该熟悉路径表达式的概念。
路径表达式最简单的定义(想想 JQuery 选择器)是用来指定处理 JSON 文档中的某一部分。
第二个要熟悉的是 JSON_EXTRACT 函数 ,它接收一个路径表达式来做为读取 JSON 数据的参数。
假设我们对至少有一个USB和HDMI端口的电视机感兴趣。
SELECT
*
FROM
`e_store`.`products`
WHERE
`category_id` = 1
AND JSON_EXTRACT(`attributes` , '$.ports.usb') > 0
AND JSON_EXTRACT(`attributes` , '$.ports.hdmi') > 0;
JSON_EXTRACT 函数的第一个参数是应用路径表达式为 attributes 对应的列的 JSON。$ 符号表示要处理的对象。 $.ports.usb 和 $.ports.hdmi 路径表达式可以分别翻译为 “获取 ports 下的 usb 的值” 和 “获取 ports 下的 hdmi 的值”。
一旦我们得到了需要的值,就可以非常简单地使用比如 “>” 的MySQL操作符了。
此外,JSON_EXTRACT 函数还有一个别名 -> ,你可以用这个别名来使你的查询语句可读性更好。
修改我们之前的查询语句。
SELECT
*
FROM
`e_store`.`products`
WHERE
`category_id` = 1
AND `attributes` -> '$.ports.usb' > 0
AND `attributes` -> '$.ports.hdmi' > 0;更新
为了更新 JSON 的值,我们将使用 JSON_INSERT, JSON_REPLACE,JSON_SET 这几个函数。这些函数还需要一个路径表达式来指定要修改的 JSON 对象的哪些部分。
这些函数的返回值是一个更改之后的合法的 JSON 对象。
下面我们来修改产品表里的 mobilephones 都有一个 chipset 的属性。
UPDATE `e_store`.`products`
SET `attributes` = JSON_INSERT(
`attributes` ,
'$.chipset' ,
'Qualcomm'
)
WHERE
`category_id` = 2;
$.chipset 变量定义了 chipset 属性的位置是在这个对象的最底部。
接下来,让我们使用 JSON_REPLACE 函数,来更新 chipset 属性,使其变的更具描述性。
UPDATE `e_store`.`products`
SET `attributes` = JSON_REPLACE(
`attributes` ,
'$.chipset' ,
'Qualcomm Snapdragon'
)
WHERE
`category_id` = 2;
十分简单!
最后,我们使用 JSON_SET 函数,我们将使用它来使产品表中的 televisions 变的丰富多彩。
UPDATE `e_store`.`products`
SET `attributes` = JSON_SET(
`attributes` ,
'$.body_color' ,
'red'
)
WHERE
`category_id` = 1;
上面提到的那些函数看起来似乎一样,但是它们的行为方式不同。
JSON_INSERT 函数只有当属性不存在的时候,它才会将这个属性添加到对象中。
JSON_REPLACE 函数只有在对象中找到该属性才会替换该属性。
JSON_SET 函数,如果在对象中没有找到这个属性,就会添加这个属性到对象中,如果对象中有这个属性了,就会替换掉原来的属性。
删除
关于删除操作我们将会关注两个点。
第一个点是从 JSON 列中删除某个 键/值,第二个点是从 JSON 列中删除某些行。
假设在商品表中我们不再提供 cameras 的 mount_type 信息,同时我们需要从商品表中移除掉所有的 cameras 的 mount_type 属性。
我们将会使用 JSON_REMOVE 函数来做删除操作,这个函数会根据路径表达式删除指定的键后返回更新的 JSON。
UPDATE `e_store`.`products`
SET `attributes` = JSON_REMOVE(`attributes` , '$.mount_type')
WHERE
`category_id` = 3;
针对第二种情况,我们在产品表中不在提供具有Android操作系统的Jelly Bean版本的 mobilephones 。
DELETE FROM `e_store`.`products`
WHERE `category_id` = 2
AND JSON_EXTRACT(`attributes` , '$.os') LIKE '%Jellybean%';
像前面所说,使用特定的某个属性需要使用 JSON_EXTRACT函数来处理,因此,为了使用 LIKE操作,我们首先提取了 mobilephones 的 os 属性(借助category_id)同时删除所有包含 Jellybean 字符串的记录。
# WEB 应用程序入门
过去直接操作数据库的日子已经一去不复返了。
如今,框架将低级操作与开发人员隔离开来,而且对于一个对框架入迷的人来说,不能将他/她的数据库知识转化为对象之间的关系映射几乎是不可能的。
为了不让这些开发人员伤心甚至去思考他们存在这个世界的意义,我们
将研究如何在 Laravel 框架中使用 JSON 列的相关业务。
我们将只关注与处理 JSON 列的主题相关关的部分。关于 Laravel 框架的深入教程超出了本文的范围。
#创建迁移文件
确定你的 Laravel 应用程序使用的是 MySQL 数据库。
我们将要为 brands,categories,products 这三个表分别创建迁移文件。
$ php artisan make:migration create_brands
$ php artisan make:migration create_categories
$ php artisan make:migration create_productscreate_brands 和 create_categories 这两个迁移文件差不多,并且这么写迁移文件也是对 Laravel 开发人员的一个规定。
/* database/migrations/create_brands.php */
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateBrands extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('brands', function(Blueprint $table){
$table->engine = 'InnoDB';
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::drop('brands');
}
}
/* database/migrations/create_categories.php */
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateCategories extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('categories', function(Blueprint $table){
$table->engine = 'InnoDB';
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::drop('categories');
}
}
create_products 迁移文件里面会有索引跟外键的申明。
/* database/migrations/create_products */
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateProducts extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('products', function(Blueprint $table){
$table->engine = 'InnoDB';
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->unsignedInteger('brand_id');
$table->unsignedInteger('category_id');
$table->json('attributes');
$table->timestamps();
// foreign key constraints
$table->foreign('brand_id')->references('id')->on('brands')->onDelete('restrict')->onUpdate('cascade');
$table->foreign('category_id')->references('id')->on('categories')->onDelete('restrict')->onUpdate('cascade');
// indexes
$table->index('brand_id');
$table->index('category_id');
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::drop('products');
}
}注意下 $table->json('attributes'); 在迁移文件中的申明。
就像使用合适的数据类型去定义其他表中的字段一样,我们使用 json 方法创建一个 名字为 attribues 的JSON 列。
而且,这只适用于支持 JSON 数据类型的数据库引擎。
这些引擎,比如老版本的 MySQL 将无法执行这些迁移。
创建模型
除了关联以外,建立模型不需要太多的东西就能让我们快速地运行起来。
/* app/Brand.php */
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Brand extends Model
{
// A brand has many products
public function products(){
return $this->hasMany('Product')
}
}
/* app/Category.php */
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Category extends Model
{
// A category has many products
public function products(){
return $this->hasMany('Product')
}
}
/* app/Product.php */
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Product extends Model
{
// Cast attributes JSON to array
protected $casts = [
'attributes' => 'array'
];
// Each product has a brand
public function brand(){
return $this->belongsTo('Brand');
}
// Each product has a category
public function category(){
return $this->belongsTo('Category');
}
}此外,我们的 Product 模型需要特别提到。
$casts 数组将键 attributes 设置为 array 以确保每次从数据库获取结果时 ,它的 attributes JSON都被转换成关联数组。
我们将在后面课程中看到如何帮助我们更新控制器动作中的记录。
#资源操作
创建一个产品
说到管理面板,因为我们有许多产品类别,所以创建产品的参数可能会通过不同的路由进入。 同时可能也会用不同的视图来创建、编辑、显示和删除产品。
例如,添加相机的表单需要与添加手机的表单输入的字段不同,因此需要确保它们能分别使用单独的视图。
此外,你一定会只想通过一个请求验证器来分别用于相机和手机的请求验证。
最后再来通过 Eloquent 创建产品。
本章节使用相机作为示例, 其他产品可以使用类似方式生成的代码进行处理。
假设我们正在保存一台相机,控制器操作将表单域中的不同品牌类型的相机的特殊字段统一放到了 attributes 字段中:
// 在数据库中创建产品
// 使用表单字段
public function store(Request $request){
// 创建对象和设置属性
$camera = new \App\Product();
$camera->name = $request->name;
$camera->brand_id = $request->brand_id;
$camera->category_id = $request->category_id;
$camera->attributes = json_encode([
'processor' => $request->processor,
'sensor_type' => $request->sensor_type,
'monitor_type' => $request->monitor_type,
'scanning_system' => $request->scanning_system,
]);
// 存入数据库
$camera->save();
// 展示已创建的相机数据
return view('product.camera.show', ['camera' => $camera]);
}读取产品Product信息
调用Product模型声明的$casts数组变量,在读取和编辑的时候会自动转换关联的数组。
// 读取单个产品信息
// 从数据库
public function show($id){
$camera = \App\Product::find($id);
return view('product.camera.show', ['camera' => $camera]);
}视图将以下方式使用$camera变量渲染数据。
<table>
<tr>
<td>Name</td>
<td>{{ $camera->name }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Brand ID</td>
<td>{{ $camera->brand_id }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Category ID</td>
<td>{{ $camera->category_id }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Processor</td>
<td>{{ $camera->attributes['processor'] }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Sensor Type</td>
<td>{{ $camera->attributes['sensor_type'] }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Monitor Type</td>
<td>{{ $camera->attributes['monitor_type'] }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Scanning System</td>
<td>{{ $camera->attributes['scanning_system'] }}</td>
</tr>
</table>编辑产品
如前所述,我们可以轻松的获取产品信息并输出到视图。接下来就是编辑视图的部分。
你可以在编辑视图的表单上预先填充好产品的信息。
根据用户的输入更新产品将与我们之前看到的 store 操作非常类似,只是不是创建新的产品,而是在更新产品前先从数据库中获取它。
基于 JSON 属性的搜索
要讨论的最后一块难题是使用 Eloquent ORM 查询 JSON 列。
如果你的搜索页面允许根据用户提供的条件搜索相机, 则可以使用以下代码进行搜索。
// 根据用户提供的条件搜索相机
public function search(Request $request){
$cameras = \App\Product::where([
['attributes->processor', 'like', $request->processor],
['attributes->sensor_type', 'like', $request->sensor_type],
['attributes->monitor_type', 'like', $request->monitor_type],
['attributes->scanning_system', 'like', $request->scanning_system]
])->get();
return view('product.camera.search', ['cameras' => $cameras]);
}现在可以将搜索结果作为$cameras集合提供给product.camera.search视图。
删除产品
如果是使用非 JSON 属性的字段,可以通过指定 where 子句再调用 delete 方法来删除产品。
例如,在使用 ID 的情况下:
\App\Product::where('id', $id)->delete();而对于 JSON 属性的字段,可以使用 where 子句指定单个或多个属性,然后调用 delete 方法。
// 删除所有属性 sensor_type 为 CMOS 的相机
\App\Product::where('attributes->sensor_type', 'CMOS')->delete();
}#结尾
如何在 MySQL 中使用 JSON 列,我们以上的内容仅仅触及表面。
无论何时,当你需要将数据保存为单独的表中的键/值对或使用实体的灵活属性时,都应该考虑使用 JSON 数据类型字段,因为它可以有益于压缩数据库设计。
如果您有兴趣深入研究, MySQL 文档是进一步探索 JSON 概念的好资源。
我希望你觉得这个教程有趣,有见地。在我下个作品前,快乐编程!
本文中的所有译文仅用于学习和交流目的,转载请务必注明文章译者、出处、和本文链接
我们的翻译工作遵照 CC 协议,如果我们的工作有侵犯到您的权益,请及时联系我们。






 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu




推荐文章: